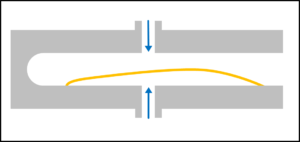
hollow cathode
rod cathode
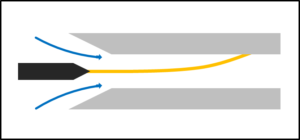
The process transforms neutral gas into a plasma state by introducing energy. High voltage across electrodes creates an electric field, energizing electrons to break free. Liberated electrons and formed ions create a plasma mixture.
Role of the Arc in Ionization:
The arc supplies essential energy for ionization.Accelerated electrons collide with neutral gas, causing further ionization. Intense heat generated by the arc adds to gas ionization, creating a highly energized plasma. Role of Carrier Gas (e.g., Argon) in Steam Plasma:
Carrier gases, like argon, facilitate and stabilize the plasma process.In steam plasma, argon carries introduced water vapor, supporting ionization and vaporized material transport. Argon, inert and non-reactive, sustains the plasma state and ensures a controlled environment. the plasma torch’s arc and carrier gas, such as argon, synergistically contribute to ionization, creating controlled and efficient processes in diverse applications.


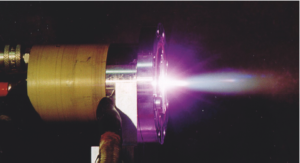 Our PB plasma torches are at the heart of our plasma systems for the disposal of pollutants and waste-to-energy processes. They were developed as a pioneering solution for the thermal treatment of waste streams and material conversions.
Our PB plasma torches are at the heart of our plasma systems for the disposal of pollutants and waste-to-energy processes. They were developed as a pioneering solution for the thermal treatment of waste streams and material conversions. The burners of the PBO series can be operated with oxidative plasma gases such as air, steam or CO2. Different sizes between 1 and 100 kW electrical power are available for different applications, such as fission plants for CFC disposal, waste treatment, conditioning of pyrolysis gases, etc.
The burners of the PBO series can be operated with oxidative plasma gases such as air, steam or CO2. Different sizes between 1 and 100 kW electrical power are available for different applications, such as fission plants for CFC disposal, waste treatment, conditioning of pyrolysis gases, etc.
 PBI burners are optimised for operation with oxygen-free gases such as hydrogen, nitrogen, ammonia, argon or helium.
PBI burners are optimised for operation with oxygen-free gases such as hydrogen, nitrogen, ammonia, argon or helium. Power supplies adapted to the torch technology are required to operate the plasma sources. PlasmaAir has developed robust sources suitable for industrial use for this purpose. The sources are current regulated and equipped with an ignition system optimised for the sources.
Power supplies adapted to the torch technology are required to operate the plasma sources. PlasmaAir has developed robust sources suitable for industrial use for this purpose. The sources are current regulated and equipped with an ignition system optimised for the sources. PlasmaAir supplies complete self-sufficiently operable plasma systems including the peripherals required for operation such as gas supply and cooling system.
PlasmaAir supplies complete self-sufficiently operable plasma systems including the peripherals required for operation such as gas supply and cooling system.